蚂蟥(Whitmania pigra)是药材水蛭基原动物之一,收录于《中国药典》(2020年版),具有抗凝、降栓等功效,水蛭及以其为主要原料的中成药是常用活血化瘀药,临床疗效十分显著。随着蚂蟥人工养殖规模和密度不断扩大,蚂蟥疾病问题突显,“红肿病”尤为突出,已成为人工养殖蚂蟥产业发展的瓶颈。
近日,贵州师范学院程搏幸副教授在Aquaculture杂志(中科院1区,TOP期刊)发表了题为《Isolation, identification and characterization of Aeromonas allosaccharophila from infected farmed leech (Whitmania pigra) in Jiangsu, China》的论文。该研究首次证明A. allosaccharophila是蚂蟥“红肿病”致病细菌性病原菌,为蚂蟥规范化养殖中细菌性疾病的防控提供重要参考依据。研究成果以贵州师范学院生物科学学院为第一完成单位,邵贵燕为文章第一作者,贵州师范学院程搏幸副教授和盐城工学院刘飞教授为文章通讯作者。邵贵燕2020年本科毕业于贵州师范学院,是我校与盐城工学院联合培养在读硕士研究生。
为厘清蚂蟥“红肿病”病因,课题组从患“红肿病”蚂蟥病灶处分离到8株细菌,经科赫氏法则验证了4株细菌是蚂蟥患“红肿病”的细菌性病原菌,其中WP204细菌致病性最强,导致蚂蟥腹部出血发红,躯干水肿和缺乏弹性(图1),肌肉组织和肠道组织均发生细胞裂解,细胞间隙变大等现象(图2)。对WP204细菌进行基因组测序分析,从粘附基因、毒力基因、抗生素耐药基因等方面解析了该细菌的致病性。联合WP204细菌外观形态、生理生化特性、核心基因组进化分析和ANI分析等方法确认该细菌为Aeromonas allosaccharophila(图3),揭示了该致病菌的生长特性(图4),通过LD50和LT50等指标明确了该菌的致病特征。
该研究得到了国家自然科学基金(82073968)、贵州师范学院博士项目(2020BS004)和大学生科研项目(2022DXS197)等项目资助。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739867

Figure 1. Comparison of healthy and diseased leech.
Note: A: healthy leech; B: death leech in leech farm; C: diseased leech of WP204 infection.
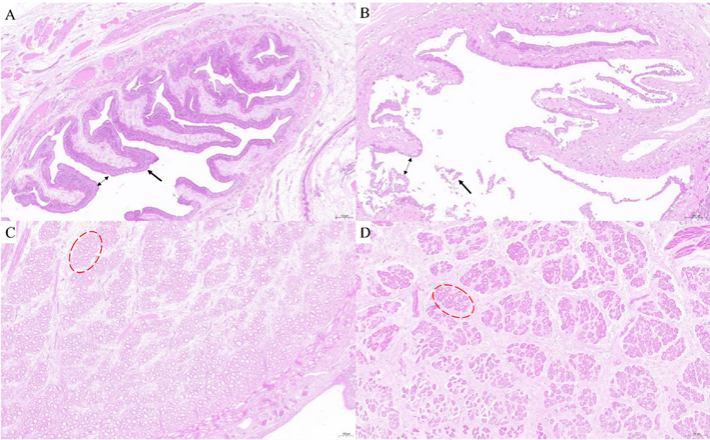
Figure 2. Tissue sections of intestine and muscle of healthy and diseased leech.
Note: A: Intestine of healthy leech; B: Intestine of diseased leech; C: Muscle of healthy leech;
D: Muscle of diseased leech.
Bidirectional arrows represent gaps in the intestine, unidirectional arrows point to changes in the intestine, and dashed ellipses circle specific morphological changes within the muscle tissue.
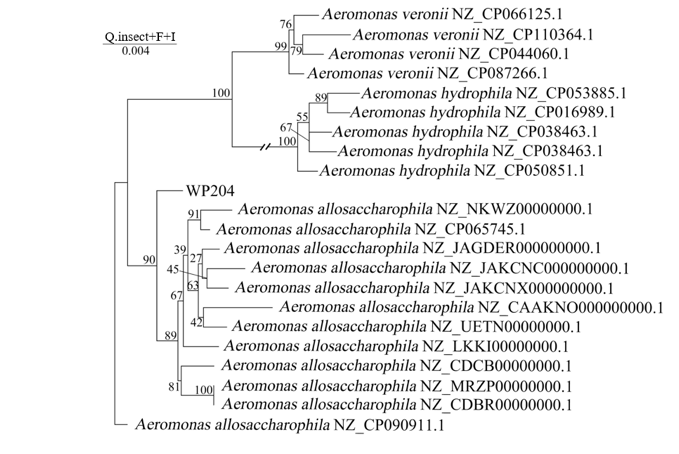
Figure 3. A Maximum Likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of the core genome of the WP204 genome.

Figure 4. Growth curves in different conditions of WP204.
Note: A: Growth curve at 28°C for 24h; B: Growth curves at different salinities C: Growth curves at different pH; D: Growth curves at different temperate.
文/梁涛 一审/王珏,二审/刘讯,三审/孙秀华
